Home » Archives for Anand » Page 6
World Geography MCQs – 03 (Types of Winds)
Types of winds MCQs with answers and explanations for all examinations.
Chapterwise MCQs
Short Notes
Free Test Series
CivilsCracker Explains
1. Which of the following combinations is/are right?
1. Winds that blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction → Local winds
2. Winds that change their direction in different seasons → Seasonal winds
3. Winds that blow only during a particular period of the day or year in a small area → Permanent winds
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) 2 and 3
Correct Answer – (b) 2 only
- There are three main types of wind as mentioned below:
- Permanent winds:
- These winds blow constantly throughout the year in a particular direction.
- The trade winds, westerlies and easterlies are the permanent Winds.
- Seasonal winds:
- These winds change their direction in different seasons. For example monsoons in India.
- Local winds:
- These blow only during a particular period of the day or year in a small area.
- Example – Land and Sea breeze, Loo( the hot and dry local wind of northern plains of India) etc.
2. The pattern of planetary winds is affected by which among the following :
1. Rotation of the earth
2. Distribution of continents and oceans
3. Emergence of pressure belts
4. Migration of pressure belts
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 & 2 only
(b) 2, 3 & 4 only
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) All of the above
- Planetary winds are a type of atmospheric circulation that occurs on a planet due to the differential heating of the atmosphere.
- The pattern of planetary winds are mainly affected by the following factors:
- Rotation of the earth
- Distribution of continents and oceans
- Emergence of pressure belts
- Migration of pressure belts
- Latitudinal variation of atmospheric heating
3. Consider the following statements:
1. The low pressure area is associated with cloudy sky and wet weather.
2. High pressure is associated with clear and sunny skies.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) Both 1 and 2
- Air pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by the weight of air on the earth’s surface.
- The air pressure is highest at sea level and decreases with height.
- Low pressure is associated with cloudy skies and wet weather.
- High pressure is associated with clear and sunny skies.
4. Consider the following statements :
1. Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by temperature of air at a given place.
2. Air always moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) Both 1 and 2
- Horizontally the distribution of air pressure is influenced by temperature of air at a given place.
- In areas where the temperature is high and the air gets heated and rises. This creates a low-pressure area which is a cause of cyclones.
- In areas having lower temperatures, the air is cold and heavy. Heavy air sinks and creates a high pressure area which results in calm weather.
- The air always moves from high pressure areas to low pressure areas.
5. Consider the following local winds and the location in which they blow:
1. Harmattan → Central and West Africa
2. Ghibli → Libya
3. Chinook → North America
Which of the above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 & 2 only
(b) 2 & 3 only
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) All of the above
- The Harmattan is a dry and dusty wind which blows from the Sahara over West and Central Africa from November to March.
- The Ghibli is a hot, dry and dusty desert wind which blows in Libya throughout the year.
- Chinook is a warm and dry wind that blows in the eastern slopes of the Rocky Mountains in North America, mainly in the winter season.
6. Consider the following local winds and the location in which they blow:
1. Abrolhos → Brazil
2. Loo → India
3. Foehn → North Italy
Which of the above are correctly matched?
(a) 1 & 2 only
(b) 2 & 3 only
(c) All of the above
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) All of the above
- Abroholos is a violent wind that blows in the south-eastern coast of Brazil mainly during May and August.
- The Loo is a hot and dry summer wind which blows over the Indo-Gangetic Plain region of North India and Pakistan.
- Foehn is a dry, warm, and fast wind which blows on the leeward side of the Alps mountain ranges. It blows in a rain shadow region and causes a significant rise in temperature. They are also called ‘Snow Eaters’ in North America.
7. Consider the following statements :
1. Anabatic Winds are downslope winds.
2. Katabatic winds are upslope winds.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (d) None of the Above
- Anabatic Winds:
- These are upslope winds.
- They blow up a mountain, driven by heating of the slope facing the sun through insolation.
- They generally blow during the daytime in calm sunny weather.
- Katabatic Winds:
- Katabatic winds are downslope winds which are created when the mountain surface is colder than the surrounding air.
- Cold mountain surface cools the wind which becomes denser and heavier and hence blows down the slope due to gravity.
8. Consider the following statements about Coriolis force:
1. It deflects the winds to the right direction in the Northern hemisphere.
2. It deflects the winds to the left direction in the southern hemisphere.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) Both 1 and 2
- Coriolis force is caused by the earth’s rotation.
- It is responsible for deflecting winds towards the right in the northern hemisphere and towards the left in the southern hemisphere.
- The deflection of the wind is more when the wind velocity is high.
9. Consider the following statements about Trade winds:
1. They flow from subtropical high-pressure belts to equatorial low-pressure belts.
2. They flow only in the Northern hemisphere and do not exist in the southern hemisphere.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (a) 1 only
- Trade winds are the permanent winds that flow from subtropical high-pressure belts to equatorial low-pressure belts.
- They flow in both the Northern and the Southern hemisphere.
- These are known as Northeast trade winds in the northern Hemisphere and southeast trade winds in the southern Hemisphere.
10. Consider the following statements about Westerlies :
1.They flow from sub-tropical high pressure belts to sub-polar low pressure belts in both hemispheres.
2. They are known as Roaring forties and Furious fifties in the Northern hemisphere due to their high speed and sound.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (a) 1 only
- Trade winds are the permanent winds that flow from subtropical high pressure belts to sub-polar low pressure belts in both hemispheres.
- They are known as Roaring forties(flows between 40º – 50ºS latitudes), Furious fifties(flows at 50ºS latitude) and Shrieking sixties(at 60ºS latitudes) in the Southern hemisphere due to their high speed and sound.
11. Consider the following statements regarding the Polar winds :
1. They flow from polar high-pressure belts to subpolar low-pressure belts in both hemispheres.
2. They are responsible for causing blizzards.
Which of the above assertions is/are true?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) None of the Above
Correct Answer – (c) Both 1 and 2
- Polar winds are the permanent winds that flow from polar high-pressure belts to subpolar low-pressure belts in both hemispheres.
- They flow at high speeds.
- Their speed is intensified during the winter season which causes blizzards.



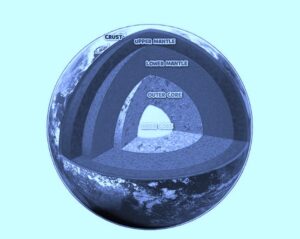 The interior of the earth can be divided into 3 different layers:
The interior of the earth can be divided into 3 different layers: never shines overhead on any latitude beyond the Tropic of
never shines overhead on any latitude beyond the Tropic of 


