Soils of Bihar | Geography of Bihar Notes
Soils of Bihar Notes of Bihar notes/study material for preparation of BPSC Prelims and Mains and other Bihar state examinations
Home » BPSC Study Materials » Geography of Bihar » Physical Features of Bihar | Geography of Bihar Notes
Physical Features of Bihar notes/study material for preparation of BPSC Prelims and Mains and other Bihar state examinations
Bihar is located in the eastern part of India. The state is surrounded by Nepal in the north, West Bengal in the east, Uttar Pradesh in the west and Jharkhand in the south.
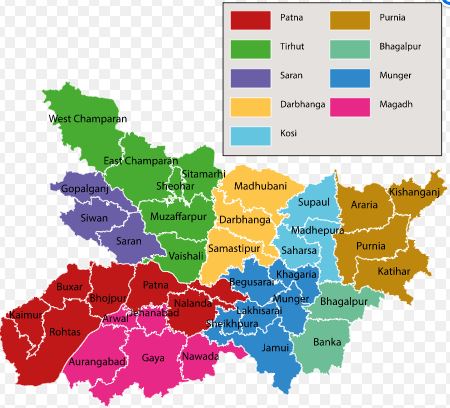
On the basis of physical features, Bihar has been divided into three parts:
You can study complete study material for BPSC here : Complete BPSC free study material

Soils of Bihar Notes of Bihar notes/study material for preparation of BPSC Prelims and Mains and other Bihar state examinations

Rivers of Bihar Notes of Bihar notes/study material for preparation of BPSC Prelims and Mains and other Bihar state examinations
We are adding new Notes, Chapterwise MCQs, Quizzes, Previous Years Questions everyday
We are adding new Notes, Chapterwise MCQs, Quizzes, Previous Years Questions everyday